Phobia
Phobia
Phobia means fear. Generally speaking, a ‘phobia’ refers to the fear of any object or situation. The object or situation may or may not necessarily pose danger but the fear is real and affects the person to an extent that there is anxiety and avoidance by the person. Phobia can be short term or long lasting and cause strong physical and psychological reactions.
In Ayurveda, Unmada covers a wide range of symptoms and is synonymous with insanity, mania etc. Phobia too, is considered under the gamut of diseases/conditions covered under Unmada or Bhayaja Unmada.
According to Ayurveda, sadhaka pitta is deemed to be essentially responsible for mental functioning and emotions. It is based in hridaya (heart/mind) and responsible for the feelings of fear (bhaya), courage, valor (shourya), anger (krodha), happiness (harsha) and intelligence (buddhi).
Hyperactivity of rajas (action) or tamas (inertia) causes the mind to lose its balance and affects the tridosha (vata, pitta, kapha) resulting in mental disorders that can manifest as a phobia.

Causes Of Phobia
Exact causes of Phobia are not known. Some known causes of developing phobias are –
- Some phobias first appear in childhood and some later in life but usually before the age of 35.
- Surroundings & family.There could be an inherited tendency of children to learn phobias by observing a family member.
- People who are more sensitive are at a higher risk of developing Phobia.
- A traumatic event.Any traumatic event can cause phobia
Symptoms Of Phobia
Phobias (Specific or social in origin) can present with the following symptoms :
- Panic or terror when facing the source of fear
- Unable to function normally
- Heavy sweating
- Fast heartbeats
- Breathlessness
Ayurvedic Treatment For Phobia
Internal Medicine
This includes the three components of chikitsa such as yukti vyapasraya (medications), daiva vyapasraya (chanting and meditation) and satvavachaya chikitsa (psychotherapy). In the first entity, aushada, ahara, vihara are properly administered as per the assessed dosha status of the condition. Here either of the sodhana chikisa or shamana chikitsa are recommended.
- Panchkarma
- Shirodhara
- Shiropichu
- Nasya
- Abhyangam
- Utavartan
- Yoga and Pranayama
- Meditation
- Counselling and psychotherapy guidence
- Mental diet plan
Diet Recommendations (Aahar)
A wholesome healthy diet is essential for mental health and happiness .
Lifestyle Changes (Vihar)
- Achar rasayan (Good behavior and lifestyle) influences the Pravar Satva (Higher mental equilibrium).
- Satvajaya chikitsa (Psychatric Councelling, mental hygiene ) may have a beneficial role in management of phobias. Intellect promoting or Medhya drugs such as Mandukaparni (Centella asiatica Linn.), Yastimadhu (Glycirrhiza glabra Linn.), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia (Wild) Miers) and Shankhapushpi (Convolvulus pleuricaulis Chois) are beneficial in these conditions.
- Yogasanasas exercise regimen are shown to be efficacious and helpful in reduction or management of stress.
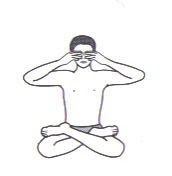
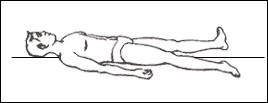
Some asanas that are helpful are as follows
- Bhramari Pranayama : Paroxysmal gamma waves produced in brain during the Bhramari Pranayama which is associated with positive thoughts, feelings of happiness and acts as a natural antidepressant .
- Shavasana : Savasana has a regenerative effect on the mind and the body. It provides relief from any kind of stress and strain in few minutes. It is a good activity for managing restlessness, insecurity, frustration, anxiety, and fear.
Diet for phobia