Child dermatology or skin desease
Dermatology is about skin health and related diseases. According to Ayurveda, healthy skin is a result of overall health condition of individuals. Ayurvedic treatment for dermatology talks about different skin care regimes that can be pursued depending on the stage of life. Ayurvedic herbs purify the skin and eliminate vitiated tridoshas from the body as they are mainly responsible for skin disorders and other diseases. Ayurveda has several natural remedies for dermatology diseases that help obtain healthy skin and glowing complexion.
Know More on Dermatology
ACNE 
Acne is defined as a skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become plugged with oil and dead skin cells. Acne usually appears on your face, neck, chest, back and shoulders.
In Ayurveda acne is termed as Mukhadushika which falls under Kshudrarogas. It is characterized as shalmali kantaka (thorn of Bombax ceiba) like eruption on the face due to vitiation of kapha, vata and rakta dosha. Since it is commonly seen in adolescents, this problem is also known as Yauvanpidika in Ayurveda; yauvan means ‘adolescence’ and pidika means ‘boils or papules
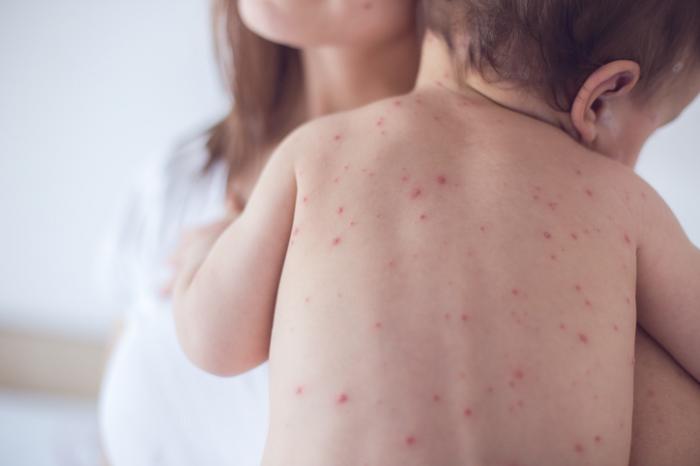
 ECZEMA
ECZEMA
Eczema is a skin condition in which the skin becomes itchy, red, dry and cracked. It’s most common in children but can occur at any age. The most common type of eczema, which can also be severe and long-lasting, is atopic dermatitis (AD). The other types of eczema are contact dermatitis (inflamed, itchy and red skin due to irritating substances or allergens), dyshidrotic eczema (small, itchy blisters on the edges of the fingers, toes, palms, and soles of the feet), hand eczema (irritant contact dermatitis on the fingers and spaces in between them), neurodermatitis or lichen simplex chronicus (thick, scaly patches on skin as a result of too much rubbing and scratching), seborrheic dermatitis (redness, itching, and dry, flaky skin localized mainly on the areas of skin that are rich in sebaceous glands), nummular eczema or discoid eczema (very itchy coin-shaped spots on skin), stasis dermatitis or venous stasis dermatitis (happens when there is a problem with blood flow in the veins and pressure develops).
In Ayurveda, the various skin disorders are detailed under the heading of Kushta. Vicharchika is specially mentioned under the heading of Kshudra Kushta (minor skin diseases) in Ayurvedic classics and it is similar to disease eczema in modern medical science.
HERPES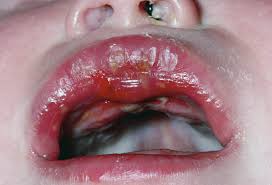
Herpes simplex is a common viral infection. It is is caused by the Herpes simplex virus (HSV) and is of two types – oral or genital Oral herpes is caused by HSV-1 virus and is exhibited as cold sores around the mouth or face. Genital herpes affects the genitals, buttocks or anal area and is caused by HSV-2. But either of HSV-1 or HSV-2 can cause a herpetic sore on the face or genitals.
Sarasapi or Sarasapika is the Ayurvedic term that can be correlated with Herpes infection, which means mustard like blisters. Shukaja Sarasapi is genital herpes and Pramehaja sarasapi is facial herpes. Both of them may have the same characteristics but the etiologies are different
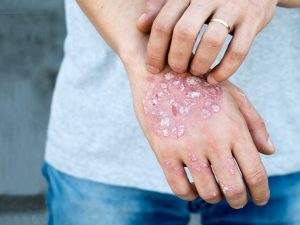
PSORIASIS
Psoriasis is a long-lasting disease which is characterized by thick, silvery scales; itchy, dry, red patches which are sometimes painful. Types of Psoriasis include Plaque psoriasis (raised, red patches covered with a silvery white buildup of dead skin cells), Guttate psoriasis (small dot like lesions), Inverse psoriasis (red lesions in body folds), Pustular psoriasis (blisters of non-infectious pus surrounded by red skin) and erythrodermic psoriasis (fiery redness all over the body).
In Ayurveda, all skin diseases can be included under the term Kushta. The word Kushta means – that which makes ones skin look disgraceful. Psoriasis is co-related with Kitibha, Sidhma or Eka kushta. Psoriasis is a krichasadhya vyadhi i.e. not fatal but causes great deal of unhappiness and depression.
 VITILIGO-LEUCODERMA
VITILIGO-LEUCODERMA
Vitiligo or leucoderma is a disease that causes the loss of skin color in blotches. This happens because the cells that make pigment (color) in the skin – the melanocytes are destroyed. The extent and rate of color loss from vitiligo is unpredictable. It affects all skin types but is more predominant in darker skin. It can affect the skin on any part of your body. It may also affect hair, the inside of the mouth and even the eyes.
In Ayurvedic classical literature, leucoderma is known as Sveta Kushtha ‘white leprosy‘ and is also called shwitra. It has of two subtypes – Kilas and Varuna depending on the skin color. An imbalance in the Vata and bhrajaka pitta (subtype of pitta that imparts color to skin) may cause skin diseases. Shwitra differs from other skin disorders by the normal functioning of all but the “skin tissue” (twak, rakta, mamsa, meda) resulting in discoloration of the skin (twak vaivarnyata), without discharge (aparisravi).
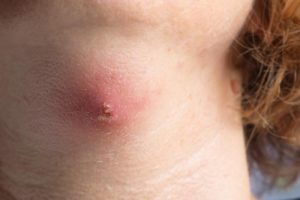 BOILS AND CARBUNCLES
BOILS AND CARBUNCLES
Boils and carbuncles are painful, pus-filled bumps forming due to bacterial infection resulting in inflammation of one or more hair follicles.1
Boils generally emerge as red, tender lumps which quickly fill with pus and grow larger and become more painful. A carbuncle is a bunch of boils forming a linked infected area beneath the skin.
Ayurveda describes carbuncle as pidaka, one of the major complications of diabetes mellitus.
MELASMA 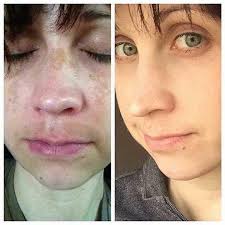
Melasma is the medical name of the condition where person has brown to grey-brown patches on cheeks, forehead, chin or above upper lip. It can also appear on other parts of body which get to much exposure to sun such as arms. Women get this disease more than men and it is commonly seen during pregnancy.
Ayurveda describes melasma as ‘Neelika’ associated with Vata, Pitta Dosha and Manasika Nidanas (psychological etiological factors) such as Krodha (anger), Shoka (sorrow), and Ayasa (mental exertion). Some believe that other conditions of skin like Vyanga (freckles) may be correlated. Freckles are hyper-pigmentation disorders of facial skin with localized discoloration.
It s classified as a Kshudraroga (minor disease) which reduces the radiant skin complexion; and is identified by the appearance of Niruja (painless), Tanu (thin) and Shavavarna Mandalas (bluish-black patches) on the face and other parts of body.
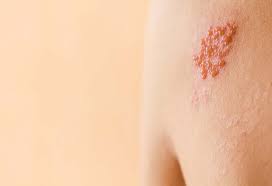 SHINGLES
SHINGLES
Shingles is a skin disease caused due to the Varicella-zoster virus, the virus that causes chickenpox. Even though any individual with a history of chicken pox is at a risk of shingles, it is most common in individuals older than 50 years of age.1
Shingles is a very agonizing skin disease characterised by vesicles on the skin surface in the form of bands.
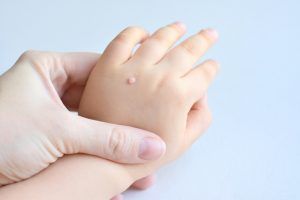 WARTS
WARTS
Warts are growths on the skin caused due to infection with human papilloma virus (HPV). Based on the region of the skin they appear, they are classified into four types:
Common warts: Appear on the fingers, are small, grainy
Plantar warts: Appear on the soles of the feet
Genital warts: Are a sexually transmitted disease
Flat warts: Appear in places that are shaved frequently
Most HPV types cause relatively less harmful conditions like common warts, but some can cause cause serious disease such as cancer of the cervix.
Ayurveda describes Warts as Charmakeela; a word derived from the words ‘charma’ and ‘keela’.
- ‘Char’ means dathu, ‘ma’ is pratyaya
- Keela means “keelyatha rudyathe sou anentra vaa”: that which pricks like a nail
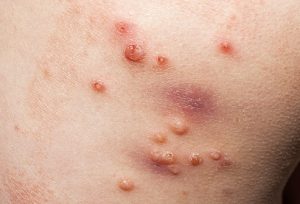 FUNGAL SKIN INFECTION -TINEA
FUNGAL SKIN INFECTION -TINEA
Fungi are organisms that make their homes in moist areas of the body where skin surfaces meet: between the toes, in the genital area, and under the breasts. These fungi grow and thrive in dead skin layers Obese and diabetics and those with weak immune system are prone to get fungal infections.
Tinea is the name of a group of contagious skin infection caused by a fungus.. Most common types of tinea include ringworm, athlete’s foot and jock itch. These infections are usually not serious, but they can be uncomfortable.1,2
At times , an allergic response to fungal infections may also occur.
In Ayurveda the term Kustha covers almost all the skin diseases. Kustha is produced invariably by the vitiation of the seven factors including the tridoshas and four Dushyas or the connective tissues; and is further categorized in to Maha kushta & Kshudra kushta. In broad sense, Kustha is the one, which causes vitiation as well as discoloration of the skin. Fungal skin infections can be classified under the aegis of Dadru Kustha -a type of Kustha that is classified under both the categories due to its quick invading nature. As per the definition, the reddish coloured Pidaka (lesion) in the form of Mandala (rounded lesion) with elevated borders and itching is known as Dadru

